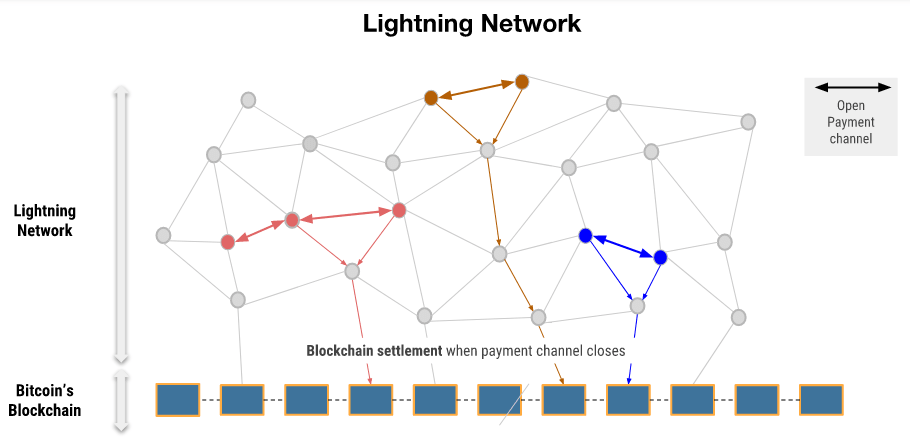
The Lightning Network is a decentralized network built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain that allows for faster and cheaper transactions. It is a payment protocol that enables instant, high-volume micropayments between two parties without the need for a third-party intermediary.
In traditional Bitcoin transactions, each transaction is recorded on the blockchain, which can take several minutes to confirm and comes with transaction fees that can be expensive, especially for small transactions. The Lightning Network addresses these issues by creating a second layer on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, where transactions can be conducted off-chain, without the need for miners to process them.
You can also read: How To Recover Metamask Wallet?
The Lightning Network works by creating payment channels between two parties, allowing them to conduct multiple transactions without recording them on the blockchain. These transactions are instead recorded on the Lightning Network, which enables instant confirmations and lower fees. The payment channels can be opened and closed at any time, and the final balance is recorded on the blockchain.
For example, if Alice wants to send Bitcoin to Bob, they can open a payment channel between them on the Lightning Network. Alice can then send Bitcoin to Bob through this channel, and the transaction will be recorded on the Lightning Network without being processed by miners. The Lightning Network will keep track of the balances, and Alice and Bob can continue to conduct transactions between them without recording them on the blockchain. If they want to close the payment channel, the final balance will be recorded on the blockchain.
More about Lightning Network
The Lightning Network also allows for multi-party payment channels, where several parties can createa payment channel between them, enabling them to conduct transactions with each other without the need for individual payment channels. This makes it possible to conduct transactions with multiple parties simultaneously, increasing the speed and efficiency of transactions.
The Lightning Network has the potential to revolutionize the way we conduct transactions on the Bitcoin network. By enabling faster and cheaper transactions, it could make Bitcoin a more viable option for everyday purchases and micropayments. However, it is important to note that the Lightning Network is still in its early stages of development and has some limitations, such as the need for both parties to be online to conduct transactions. Nonetheless, with ongoing development and improvements, the Lightning Network has the potential to significantly improve the usability and accessibility of Bitcoin.
How Fast Is Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network is designed to be a fast and efficient payment protocol that enables instant transactions between two parties. It is built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain and operates independently of the underlying blockchain, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions.
One of the main benefits of the Lightning Network is its speed. Transactions on the Lightning Network can be conducted instantly, without the need for confirmations on the blockchain. This is because transactions on the Lightning Network are conducted off-chain, allowing for faster confirmation times and lower fees.
To understand the speed of the Lightning Network, it’s important to understand how it works. The Lightning Network creates payment channels between two parties, allowing them to conduct multiple transactions without recording them on the blockchain. These transactions are instead recorded on the Lightning Network, which enables instant confirmations and lower fees. The payment channels can be opened and closed at any time, and the final balance is recorded on the blockchain.
For example, if Alice wants to send Bitcoin to Bob, they can open a payment channel between them on the Lightning Network. Alice can then send Bitcoin to Bob through this channel, and the transaction will be recorded on the Lightning Network without being processed by miners. The Lightning Network will keep track of the balances, and Alice and Bob can continue to conduct transactions between them without recording them on the blockchain. If they want to close the payment channel, the final balance will be recorded on the blockchain.
The speed of the Lightning Network depends on several factors, such as the number of nodes on thenetwork, the size of the payment channel, and the distance between the two parties. In general, the Lightning Network is designed to be very fast and efficient, with transaction times measured in milliseconds.
In fact, the Lightning Network is one of the fastest payment protocols available today. It is much faster than traditional Bitcoin transactions, which can take several minutes to confirm. With the Lightning Network, transactions can be conducted instantly, making it ideal for micropayments and other types of fast transactions.
However, it’s important to note that the speed of the Lightning Network can vary depending on the specific circumstances. For example, if there are network congestion issues or if the payment channel is very large, transactions may take slightly longer to complete. Additionally, the speed of the Lightning Network may be influenced by other factors such as the quality of the internet connection and the processing power of the hardware being used.
Despite these potential limitations, the Lightning Network is generally considered to be one of the fastest and most efficient payment protocols available today. As development continues and more nodes are added to the network, it is likely that the speed and efficiency of the Lightning Network will continue to improve, making it an even more attractive option for fast and secure transactions.
How Low Are The Transaction Fees?
The Lightning Network is designed to be a low-cost payment protocol that allows for fast and efficient transactions between two parties. One of the main benefits of the Lightning Network is its ability to reduce transaction fees, making it an attractive option for micropayments and other low-value transactions.
In traditional Bitcoin transactions, the fees can be high, especially for small transactions. This is because the fees are based on the size of the transaction and the competition for block space on the Bitcoin blockchain. As a result, fees can vary widely depending on network congestion and other factors.
The Lightning Network addresses these issues by creating a second layer on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, where transactions can be conducted off-chain without the need for miners to process them. This allows for lower fees and faster confirmation times compared to traditional Bitcoin transactions.
To conduct a transaction on the Lightning Network, users need to open a payment channel between two parties. This payment channel allows for multiple transactions to be conducted without being recorded on the blockchain. Instead, the transactions are recorded on the Lightning Network, which keeps track of the balances between the two parties.
Because transactions on the Lightning Network are conducted off-chain, the fees are much lower than traditional Bitcoin transactions. In general, the fees for Lightning Network transactions are measured in satoshis, which are the smallest unit of Bitcoin. The fees can be as low as one satoshi, making it possible to conduct microtransactions and other low-value transactions with minimal fees.
In fact, the Lightning Network is oneof the most cost-effective payment protocols available today. The fees for Lightning Network transactions are typically a fraction of the fees for traditional Bitcoin transactions. This makes it an attractive option for merchants and individuals who want to conduct low-value transactions, such as buying a cup of coffee or paying for online content.
In addition to lower fees, the Lightning Network also allows for greater scalability and throughput compared to traditional Bitcoin transactions. This means that the network can handle a much higher volume of transactions at a lower cost, making it a more efficient and cost-effective payment protocol.
However, it’s important to note that the fees for Lightning Network transactions can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the payment channel, the distance between the two parties, and network congestion. In some cases, the fees for Lightning Network transactions may be higher than traditional Bitcoin transactions, especially if the payment channel is large or if there is significant network congestion.
So, the Lightning Network is a low-cost payment protocol that offers significant benefits over traditional Bitcoin transactions. By reducing fees and increasing scalability, it could make Bitcoin a more viable option for everyday purchases and micropayments. As development continues and more merchants and individuals adopt the Lightning Network, it is likely that the fees will continue to decrease, making it an even more attractive option for fast and low-cost transactions.
Is Lightning Network Cross BlockChains?
The Lightning Network is primarily designed to work with the Bitcoin blockchain, but it is also possible to use the Lightning Network to conduct transactions across different blockchains. This capability is known as cross-chain atomic swaps.
Cross-chain atomic swaps allow users to exchange cryptocurrencies across different blockchains without the need for a centralized exchange or intermediary. This is achieved by creating payment channels between two parties on different blockchains, allowing them to conduct transactions without relying on a third party.
For instance, if Alice wants to exchange Bitcoin for Litecoin with Bob, they can create a payment channel between them on the Bitcoin and Litecoin blockchains. Alice can then send Bitcoin to Bob through the Bitcoin payment channel, while Bob sends Litecoin to Alice through the Litecoin payment channel. Because the payment channels are connected, the exchange can be conducted atomically, meaning that either the entire exchange occurs or none of it does.
Cross-chain atomic swaps on the Lightning Network offer several benefits. They allow for decentralized and trustless exchanges between different cryptocurrencies, without the need for centralized exchanges that can be vulnerable to hacking or other security issues. Additionally, cross-chain atomic swaps can be conducted with minimal fees, making them an attractive option for users who want to exchange cryptocurrencies without incurring high costs.
However, it’s important to note that cross-chain atomic swaps on the Lightning Network are still in their early stages of development and can be technically challenging to implement. Different blockchains have different protocols and requirements, and creating payment channels between them requires specialized knowledge and expertise.
Despite these challenges, there has been significant progress in developing cross-chain atomic swaps on the Lightning Network. Several projects and platforms have emerged that enable cross-chain atomic swaps, such as Komodo, Blocknet, and Lightning Labs.
In addition to enabling cross-chain atomic swaps, the Lightning Network also has the potential to facilitate interoperability between different blockchains. This means that different blockchains could communicate and transact with each other, enabling the exchange of value and data across different networks. Interoperability on the Lightning Network could significantly enhance the usability and functionality of blockchain technology, allowing for new use cases and applications.
While the Lightning Network was primarily designed to work with the Bitcoin blockchain, it is possible to use it to conduct transactions across different blockchains through cross-chain atomic swaps. As development continues and more projects and platforms emerge, it is likely that cross-chain atomic swaps on the Lightning Network will become more accessible and user-friendly, enabling greater interoperability and exchange between different blockchains.
How Does Lightning Network Work?
The Lightning Network is a decentralized payment protocol that operates on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. It is designed to enable fast and efficient transactions between two parties without the need for intermediaries. The Lightning Network works by creating payment channels between two parties, allowing them to conduct multiple transactions without being recorded on the blockchain. This allows for faster confirmation times and lower fees compared to traditional Bitcoin transactions.
To use the Lightning Network, users need to open a payment channel between two parties. This is done by creating a multi-signature address on the Bitcoin blockchain, where both parties contribute funds to the address. Once the funds are in the multi-signature address, the payment channel is opened, and the two parties can conduct transactions between them without being recorded on the blockchain.
For example, if Alice wants to send Bitcoin to Bob, they can open a payment channel between them on the Lightning Network. Alice can then send Bitcoin to Bob through this channel, and the transaction will be recorded on the Lightning Network without being processed by miners. The Lightning Network will keep track of the balances, and Alice and Bob can continue to conduct transactions between them without recording them on the blockchain. If they want to close the payment channel, the final balance will be recorded on the blockchain.
The Lightning Network also supports multi-party payment channels, allowing multiple parties to create a payment channel between them. This enables them to conduct transactions with each other without the need for individual payment channels. This makes it possible to conduct transactions with multiple parties simultaneously, increasingthe speed and efficiency of transactions.
To ensure the security of the Lightning Network, each transaction on the payment channel is signed by both parties using their respective private keys. This ensures that only the two parties involved in the transaction can access the funds in the payment channel. Additionally, the Lightning Network uses a system of penalty transactions to prevent fraud or malicious behavior.
One of the key benefits of the Lightning Network is its ability to enable instant transactions. Because transactions on the Lightning Network are conducted off-chain, they can be confirmed instantly without the need for confirmations on the Bitcoin blockchain. This makes it possible to conduct fast and efficient transactions, particularly for micropayments and other low-value transactions.
In addition to enabling fast and efficient transactions, the Lightning Network also has the potential to improve the scalability and throughput of the Bitcoin network. By enabling multiple transactions to be conducted off-chain, the Lightning Network can handle a much higher volume of transactions compared to traditional Bitcoin transactions.
What’s wrong with the Lightning Network?
While the Lightning Network is an innovative and promising payment protocol, there are also several potential issues and challenges that need to be addressed. Some of the main concerns with the Lightning Network include:
- Complexity: The Lightning Network is a complex protocol that requires specialized knowledge and expertise to use and implement. This complexity can make it difficult for new users and merchants to adopt the Lightning Network, potentially limiting its adoption and use.
- Centralization: While the Lightning Network is designed to be a decentralized payment protocol, there are concerns that it could become centralized over time. This could happen if a few large nodes or payment providers dominate the network, potentially compromising its security and reliability.
- Technical challenges: The Lightning Network is still in its early stages of development, and there are still some technical challenges that need to be addressed. For example, routing payments through the network can be technically challenging, and there is a risk of payment channels becoming unbalanced.
- User experience: While the Lightning Network offers several benefits, the user experience can be challenging for some users. This is because the Lightning Network requires users to manage their own payment channels, which can be confusing and time-consuming.
- Security: While the Lightning Network is designed to be a secure payment protocol, there is always a risk of security vulnerabilities and attacks. For example, if a node on the network is compromised, it could potentially compromise the security of the entire network.
Despite these potential issues and challenges, the Lightning Network is still considered to be a promising payment protocol that offers significant benefits over traditional Bitcoin transactions. Many of the concerns with the Lightning Network are being actively addressed by developers and the broader community, and there are ongoing efforts to improve the protocol and make it more accessible and user-friendly.
To address concerns around complexity, there are ongoing efforts to develop more user-friendly Lightning Network wallets and interfaces that can make it easier for users to manage their payment channels. Additionally, there are ongoing efforts to make the routing of payments through the network more efficient and reliable.
To confront issues around centralization, there are ongoing efforts to encourage a more decentralized network by promoting the use of smaller nodes and payment providers. Additionally, there are ongoing efforts to develop incentives for users and payment providers to promote decentralization.
In order to solve concerns around security, there are ongoing efforts to improve the security of the Lightning Network by identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities and attacks. Additionally, there are ongoing efforts to develop new security protocols and features that can enhance the security and reliability of the network.
In conclusion
The Lightning Network is a promising technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we conduct transactions. It offers fast, cheap, and efficient transactions that are not possible on traditional blockchain networks. However, it is still in the early stages of development, and there are several challenges that need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted.